








MIDWEEK UPDATE 13 OCTOBER 2022Google Banner Ad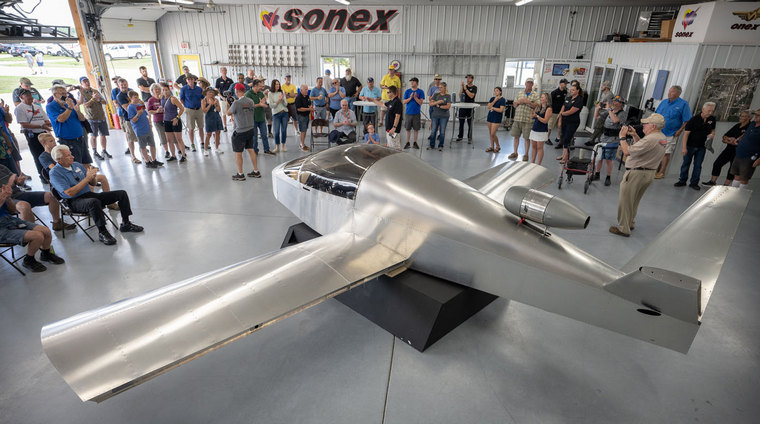             The long-anticipated Two-Seat SubSonex JSX-2T was unveiled at record-breaking EAA AirVenture Oshkosh 2022, providing the first opportunity for the public to see the new jet prototype. JSX-2T was first unveiled during the Sonex Open House and Homecoming Fly-In the day before AirVenture began and was then moved to the Sonex exhibit booth on AirVenture grounds where it was on display during the show. Sonex is in the process of lowering the turtledeck and aft canopy bow by approximately 3.5 inches. The forward canopy/windshield bow will be lowered approximately 2.2 inches to suit the aircraft's new lines while retaining a good forward sight line. This change will still fit our very tall and long-torso'd employee, James, who is 6'4" tall with only a 30" inseam. In addition to sleeker aesthetics for JSX-2T, the change will reduce structural weight for the airframe, helping us to meet our empty weight targets and will more importantly reduce frontal area and improve flow to the PBS TJ100 engine intake. While we're not changing any previously published performance estimates, these changes will help ensure that those estimates can be met or perhaps exceeded. As of this writing, progress in constructing the SubSonex JSX-2T prototype has taken a step backward to integrate this change. The original turtledeck, canopy and windshield have been removed from the aircraft, and the tail has been removed to access the aft-most fasteners in the turtledeck. Flat patterns for the new turtledeck formers have been cut and tooling for our hydro-press is in progress to form these parts, and the new turtledeck skins have been cut. We should have the new turtledeck back on the aircraft very soon and part files for new canopy bows are being sent to our machinist. Kitplanes editor and JSX-2 customer Paul Dye, while not especially tall, was absolutely swimming in the giant cockpit of the JSX-2T prototype at AirVenture, even with a 2" thick seat cushion. Sonex staff member Nathan is 6 foot, 2 inches tall with a 34 inch inseam and still has approximately 5.5 inches of clearance to the canopy.  Another change vs. what was displayed at AirVenture 2022: The instrument panel and glare shield will get the rounded profile shown in JSX-2T CAD renderings, and the forward end of the glare shield will meet the bottom of the windshield similar to our B-Model aircraft. The faceted instrument panel and glare shield shape seen on JSX-2T at AirVenture was installed merely in the interest of time to get the jet ready to display at the show.  Tecnam announced today the introduction of the new P2012 STOL dedicated to Short Take Off and Landing (STOL) operations, specifically designed to operate across the most demanding commercial airports in the world. Addressing the needs of a market niche that was left undeveloped and unsupported for decades, Tecnam is once again providing a solution to those operators that seek for their business a modern, spacious, comfortable, safe yet stylish aircraft, with outstanding STOL capabilities. The P2012 STOL is the only twin piston with Short Take-Off Landing capabilities compliant to the latest certification amendments. It offers a 3680 kg / 8113 lb Maximum Gross Weight, while guaranteeing a modern design, wide and comfortable cabin, and 11 seats. The interior accommodation is enhanced by a central aisle, a dedicated window for each of the 9 single passengers, no bench/double seats and the best passengers' amenities such as USB ports, cabin Air Conditioning, individual fresh and hot air outlets, dedicated reading light, seat pockets and cup-holders. The interior design and the superb view provided by the "high wing" configuration provide a "best-in-class" experience for the flights to typical "exotic" STOL destinations. Mission accomplishment and flight safety enhancement pass through a modern cockpit with latest technology, including state-of-the-art G1000 NXi avionic system and GFC700 specifically tuned autopilot. Active and connected flight deck (Bluetooth, flight stream, Iridium) and a toolbox of modern aids (Wx radar, storm scope, inset map, Synthetic Vision™) are provided to reduce workload and fatigue while increasing mission effectiveness. From a comfort perspective the P2012 STOL offers a +34% wider cabin, +24% larger seat pitch, +188% higher luggage weight allowance and +303% better luggage volume when compared to the most known British STOL aircraft, and does it all in accordance with the latest certification standards. Google Banner Ad From the performance perspective the P2012 STOL can easily and more comfortably carry an equivalent payload of the most known British STOL aircraft while matching its take-off and landing performances, moreover, the P2012 STOL can also outperform its useful load by 20% up to a remarkable value of 1284 kg / 2830 lb while performing a STOL mission. At Maximum Take-off Weight of 3680 kg / 8113 lb, the take-off run takes only 275 m / 900 ft and to clear the obstacle the take-off distance is achieved in just 425 m / 1395 ft. Even better at the 3630 Kg Maximum Landing Weight where the landing distance from the obstacle takes only 360 m / 1180 ft and the impressive ground run requires just 155 m / 510 ft. There are thousands of regional and local STOL airports around the world needing an outclassing airframe, superior performances, the latest safety and a 21st Century design, capable of lifting off from prepared and unprepared strips of less than 300 m / 1000 ft. The P2012 STOL, developed by the renowned and innovating Tecnam Research and Development team, is available in the passenger and multi-mission configurations (combi, cargo, air ambulance). Fully interchangeable, the 11-seat, twin-engine, fixed gear, unpressurized Tecnam can quickly and easily be converted from a 9-passenger carrier into a special-purpose aircraft… and back again.  Guy Martin defenceWeb  Asisguard said the Songar deliveries were concluded on 15 September, but did not reveal further details. In May it was reported by Africa Intelligence that Nigeria had ordered ten Songars. It is believed the contract was signed in 2021, as Asisguard last year announced contracts had been signed with two African countries and negotiations were underway with a third. Unveiled in 2019, the Songar multi-copter can be fitted with a machinegun, 40 mm grenade launcher or 81 mm mortar. It can also be fitted with a day/night camera gimbal and laser range finder. An electronic sight and ballistic calculation module assists with weapon deployment and recoil management. If using a 5.56 mm assault rifle, the Songar can carry 200 rounds of ammunition and hit a 15 square centimetre target from 200 metres away with single shots, 15-round bursts or fully automatic fire. When carrying a grenade launcher, four rounds can be fired. Google Banner Ad The 25 kg drones use a four-armed carbon body design with two coaxially mounted propellers on each arm. A weapon is fitted to a tilting mount, allowing a remote operator to aim it. Flight time is up to 25 minutes for the gun-equipped version and 15 minutes for the grenade launcher version. The Nigerian police are expected to use the Songar against armed gangs and bandits, which have recently caused havoc in several states. The Nigerian Police Force has also recently taken delivery of ALTI Transition UAVs from South Africa, and Elistair Orion fixed-wing aircraft from France. More recent UAV deliveries to Nigeria include at least four AR-500B shipborne unmanned helicopters from China. It is not yet clear if these will be used aboard Nigerian Navy vessels or from land bases. Photos emerged in September of four AR-500Bs in Nigerian Navy markings. The AR-500B, developed specifically for shipborne operations by state-owned Aviation Industry Corporation of China (AVIC), first flew in late 2020. It has a maximum take-off weight of 500 kilograms, a mission payload of 70 kilograms, a maximum endurance of four hours, an operational radius of 100 kilometres and a ceiling of 4 000 meters. It can fly at a cruise speed of 120 km/h. Nigeria's military is also getting Bayraktar TB2 UAVs from Turkey - it has been reported that Nigeria ordered six UAVs and two ground stations. Photos posted online in September showed several of the UAVs on the Baykar factory floor in Nigerian markings. Nigeria joins a rapidly growing list of Bayraktar TB2 operators in Africa. One of the most recent customers is Djibouti, which revealed its TB2s in June, while Niger received six in May after a November 2021 order for the type. Turkey has sold its Bayraktar TB2 to Ethiopia, Ukraine, Morocco, Qatar, Kyrgyzstan, Libya, Turkmenistan, Azerbaijan and Poland. Google Banner Ad The Bayraktar TB2 has a cruising speed of 130 km/h with an operational altitude of 7 300 metres and 27 hours endurance (communications range is around 300 km). The 12 metre wingspan aircraft has a maximum take-off weight of 700 kg and can carry a 150 kg payload. It is powered by a Rotax 912 engine and can be fitted with a swappable electro-optical/infrared/laser designator or multi-purpose AESA radar. The Bayraktar TB2 is used operationally by the Turkish Armed Forces and is able to employ MAM and MAM-L guided munitions and UMTAS missiles (four munitions can be carried at a time). It has been proven in combat by Turkey in Syria and Libya, where Turkey backed the Tripoli-based government against eastern forces supported by Russia, the United Arab Emirates and Egypt. In Nagorno-Karabakh, the UAVs helped Turkey's ally Azerbaijan defeat Armenia-backed forces and in Ukraine the Bayraktar TB2 has been used successfully against Russian invaders.  Guy Martin defenceWeb A Su-25 combat aircraft operated by Mali's Air Force has crashed, killing the Russian pilot. Mali's Armed Forces said the aircraft (TZ-20C) crashed near Gao Airport on 4 October after returning from a mission in the area, forcing a temporary closure of the airport. Reuters reported that two army personnel (one pilot and one on the ground) were killed and 10 people (two civilians and eight military personnel) injured in the incident, with two in a serious condition. A military official told Agence France Presse that the pilot was Russian. Video provided to AFP by a witness showed an aircraft descending at high speed before crashing in a plume of smoke. Mali's armed forces said an investigation had been launched, but there was no indication that the crash was caused by hostile action. The crashed aircraft is one of several that were recently delivered to Mali. On 9 August, Mali's armed forces commissioned one Su-25 jet, four L-39 jet trainers, a Mi-24P attack helicopter, a Mi-8 transport helicopter and a single Airbus C295 tactical transport aircraft. The C295 aircraft arrived on 31 May and is the second to be acquired, with the first delivered in December 2016. Two Mi-24Ps were delivered to Mali on 30 March this year, along with Protivnik-GE/59N6-TE mobile radars from Russia. Mali also recently acquired four Mi-35s from Russia. According to the Stockholm International Peace Research Institute's arms transfers database, Mali in 2020 ordered four Mi-8MT/Mi-17Sh helicopters from Russia for $61 million including training and weapons, with deliveries from 2021. The Su-25s and L-39s appear to be new acquisitions as well. Mali has been battered by an extremist campaign that began in the north of the country in 2012, with attacks spreading into Niger and Burkina Faso as well. As a result, Mali has turned to Russia to supply equipment and paramilitary forces to shore up its military.   Airbus Helicopters and Korea Aerospace Industries (KAI) have delivered the first Light Civil Helicopter (LCH) to a local operator, Gloria Aviation, following certification in September this year. Entering service in an emergency medical services configuration in December this year, this helicopter will be deployed to support critical life-saving missions in Jeju. This key milestone came on the back of a successful industrial partnership which started in 2015 when the two companies jointly collaborated on the LCH and Light Armed Helicopter (LAH) development programmes. The LCH completed prototype flights at the end of 2019. Other than its first application for emergency medical services, the helicopter will also be capably deployed for public service missions such as search and rescue, utility, law enforcement, and firefighting. The LAH prototype completed its maiden flight in July 2019, with the aircraft to be qualified in the coming weeks. This successful qualification will pave the way for serial production of the helicopter, which Airbus and KAI will jointly embark on by the end of 2022, for the Republic of Korea Army. "KAI has been a long-time partner to Airbus on several strategic helicopter development programmes. We are happy to celebrate this first LCH delivery which will, with the upcoming LAH qualification, kick-start a new chapter for our partnership as we enter the serial production phase," said Bruno Even, CEO of Airbus Helicopters. "We are also pleased to take our partnership a step further to prepare for the development of new variants that do not just meet the operational requirements of the end-user, but one that would bring tremendous technical and economic benefits to the local aerospace industry for years to come." Building on the successful completion of the LAH development, Airbus and KAI are preparing new joint development programmes. These helicopter programmes will leverage Airbus' technical know-how in the field of helicopter drive systems and flight control systems, while tapping into KAI's established local industrialisation expertise in the country. The two companies first started their long-standing industrial partnership in 2006 when both parties jointly worked on the Korean Utility Helicopter, followed by the LCH/LAH development programmes. The LCH/LAH are next-generation 5-tonne class helicopters that have been developed to meet Korea's requirements for local deployment in both civil and military sectors. The enduring partnership between the two parties has also seen the delivery of over 250 kits to KAI to-date, with additional orders for future deliveries.  The U.S. Army is continuing to modernize its heavy-lift helicopter fleet with an order for two more Boeing [NYSE: BA] CH-47F Block II Chinooks and long lead funding for additional aircraft. "Modernising the Chinook for our Army customer is a priority," said Ken Eland, Boeing Vice President and H-47 Program Manager. "CH-47F Block II improves readiness, limits future sustainment costs and provides commonality across the fleet. We're dedicated to making CH-47F Block II the best option for the Army's heavy lift mission, now and well into the future." The CH-47F Block II Chinook is powered by cutting-edge technologies - including redesigned fuel tanks, a strengthened fuselage and an enhanced drivetrain. Last year, the Army awarded Boeing a $136 million contract for the first four CH-47F Block II aircraft, which began production in April 2022. The Lot 2 order valued at $63 million brings the total number of aircraft under contract to six. The separate Lot 3 advance procurement contract is valued at $29 million. Boeing's H-47 Chinook Block II expands upon 60 years of partnership with the U.S. Army. During that time, Boeing has delivered over 1,000 Chinooks to the U.S. Army, continuously modernising the helicopter to meet evolving needs. The U.S. Army and 19 allied countries around the globe rely on the Chinook for its multi-mission capabilities including equipment and troop transport, humanitarian assistance and disaster relief.  <iframe width="760" height="409" src="https://www.youtube.com/embed/dtxJNlfLl0s" title="Paris Air Forum 2021: First Flight in France | Volocopter" frameborder="0" allow="accelerometer; autoplay; clipboard-write; encrypted-media; gyroscope; picture-in-picture" allowfullscreen> M3 Systems, Air Traffic Management (ATM) and unmanned aerial systems (UAS) operator, light and electric aircraft manufacturer, Pipistrel, and Volocopter, the pioneer of urban air mobility (UAM), have completed their first joint flight test campaign in France at Pontoise Airfield. The week-long flight tests simulated three different avoidance manoeuvres in real-world situations where unforeseen circumstances occur, such as a complete airport or vertiport closure, an unavailable final approach and take-off (FATO) area, and traffic deconfliction. This joint campaign between the three companies and the French partners, Groupe ADP and its wholly-owned subsidiary Hologarde, aimed to achieve smooth interaction within and between the new lower airspace's unmanned traffic management (UTM) and standard civil aviation ATM systems. The aviation industry is experiencing an innovation upsurge driven by technology and societal pressure for new forms of aviation focused on sustainable, digital, and autonomous air mobility. The resulting solutions that cater to this industry shift will generate a significant increase in traffic density in the aforementioned lower airspace. Since existing ATM systems are not designed to handle such volumes or digitalisation, harmonising existing and new traffic management systems for brand-new aircraft integration will ensure efficient large-scale operations. This includes commercial, general and drone aircraft for cargo and passenger flights, both crewed and uncrewed. The CORUS-XUAM project, funded by the European Union's initiative Single European Sky ATM Research (SESAR) Joint Undertaking, focuses on solving the challenge of conventional and new traffic management system integration and consists of 19 partners and 11 related third parties. M3 Systems, Pipistrel, and Volocopter all completed individual flight test campaigns prior to this event in order to bring their aircraft in line with the U-space services. The CORUS-XUAM flight test conducted at Pontoise Airfield near Paris is the third of several flight tests to simulate a variety of real-world scenarios that demonstrate how UTM and ATM intersect with multiple aircraft types. Moreover, the CORUS-XUAM project will continue to proactively test and create a safe and controlled lower airspace under the European Union's ambitious Single European Sky (SES) initiative throughout 2022. The successful flight tests at Pontoise Airfield were conducted with M3 System's BOREAL remotely piloted aircraft system, Pipistrel's crewed Velis Electro, the only type-certified electric aircraft in commercial service in the world and Volocopter's full-scale, remotely piloted 2X prototype. Pipistrel uses the conventional ATM tower and system while Volocopter and M3 Systems use the UTM system.  Textron Aviation Inc. announced it has been awarded a contract by the Queensland Police Service for five Beechcraft King Air 360 turboprop aircraft with heavy weight, cargo door and extended range options. The Beechcraft King Air fleet will support the Queensland Police Service law enforcement mission and be based in Brisbane, Australia. Deliveries are expected to occur through 2023. The King Air continues to be selected for a wide range of special mission roles around the world due to the aircraft's capabilities and reliability. Bob Gibbs, vice president, Special Mission Sales: "We're honoured the Queensland Police Service has chosen the Beechcraft King Air to support their law enforcement mission," said Bob Gibbs, Vice President, Special Mission Sales for Textron Aviation. "The King Air continues to be selected for a wide range of special mission roles around the world due to the aircraft's capabilities and reliability." The King Air 360 aircraft will be equipped with a gravel landing protection kit and configured in a high-density seat transport configuration. When government, military and commercial customers want airborne solutions for critical missions, they turn to Textron Aviation. The company's aviation solutions provide the high performance and flight characteristics required to address the unique challenges of special mission operations. With unparalleled quality, versatility and low operating costs, Textron Aviation products are preferred for air ambulance, ISR, utility transport, aerial survey, flight inspection, training and a number of other special operations. More than 7,700 Beechcraft King Air turboprops have been delivered to customers around the world since 1964, making it the best-selling business turboprop family in the world. The worldwide fleet has surpassed 62 million flight hours in its 58 years, serving roles in all branches of the U.S. military and flying both commercial and special mission roles around the world. .jpg)  Loss of Control at Take-off Air Methods Corporation Airbus Helicopters AS350 B3e ??On 3 July 2015, about 13:39 mountain daylight time, an Airbus Helicopter, AS350 B3e helicopter, N390LG, registered to and operated by Air Methods Corporation, lifted off from the Summit Medical Centre Heliport, Frisco, Colorado and then crashed into a parking lot; the impact point was located 360 feet southwest of the ground-based helipad. The pilot was fatally injured, and the two flight nurses were seriously injured. The helicopter was destroyed by impact forces and a post-crash fire. The flight was conducted under the provisions of 14 Code of Federal Regulations Part 135 on a company flight plan. Visual meteorological conditions prevailed at the time of the accident. The AS350 B3e has a dual hydraulic system. The upper and lower hydraulic systems provide hydraulic assistance to the main rotor flight controls. This dual-hydraulic setup provides redundancy to the main rotor servo controls in case one of the hydraulic systems were to fail. The lower hydraulic system provides hydraulic assistance to the tail rotor flight controls. Because the tail rotor system has only a single-cylinder servo control, a yaw load compensator provides continuous hydraulic power assistance to the pedal controls in the event of a loss of pressure to the lower hydraulic system. Operational procedures for the AS350 B3e required the pilot to perform a pre-flight hydraulic check to ensure that the yaw load compensator was functional. The steps of the check involved (1) moving the yaw servo hydraulic switch to the "OFF" position (which cuts off hydraulic pressure to the tail rotor hydraulic circuit) and then ensuring that pedal forces remained low; (2) depressing a test button on the cockpit center console, thereby releasing (depleting) the hydraulic pressure in the yaw load compensator accumulator by opening its solenoid valve, and then ensuring that loads were felt on the pedals; (3) resetting the test button, thereby closing the solenoid valve; and (4) restoring hydraulic pressure by moving the yaw servo hydraulic switch to the "ON" position. The National Transportation Safety Board's (NTSB) investigation determined that the pilot most likely did not return the yaw servo hydraulic switch to its "ON" position before take-off, resulting in no hydraulic pressure in both the tail rotor servo control and the yaw load compensator accumulator, a lack of hydraulic boost to the pedals, and significantly increased pedal loads. Surveillance videos capturing the lift-off showed the helicopter yaw to the left and rotate counter clockwise several times before descending and impacting a recreational vehicle and the parking lot. Video evidence also showed that the pilot did not perform a hover check, as required by operational procedures, which could have allowed the pilot to verify the helicopter's controllability. A surveillance video capturing the helicopter's descent and ground impact showed fuel flowing from the wreckage just after impact and then the onset of a post-crash fire. The post-crash fire consumed or severely damaged most of the helicopter and resulted in extensive thermal injuries to the pilot and one of the flight nurses. Although the helicopter was manufactured in March 2013, it was not subject to the improved crashworthiness requirements regarding crash-resistant fuel systems that became effective in November 1994. The helicopter was not subject to these requirements because it was certificated according to the regulations that were in effect in December 1977, when the Federal Aviation Administration (FAA) provided initial type certificate design approval for AS350-series helicopters. In addition, although the helicopter was not required to be equipped with a flight recorder system, Air Methods voluntarily equipped the helicopter with an onboard image recorder. However, this recorder did not comply with the crash-resistance provisions of an FAA technical standard order (TSO) addressing the minimum performance standards for lightweight flight recorder systems and the NTSB was unable to recover data from the recorder due to impact and post-crash fire damage. What We Found ?The probable cause of this accident was Airbus Helicopters' dual-hydraulic AS350 B3e helicopter's (1) pre-flight hydraulic check, which depleted hydraulic pressure in the tail rotor hydraulic circuit, and (2) lack of salient alerting to the pilot that hydraulic pressure was not restored before take-off. Such alerting might have cued the pilot to his failure to reset the yaw servo hydraulic switch to its correct position during the pre-flight hydraulic check, which resulted in a lack of hydraulic boost to the pedal controls, high pedal forces and a subsequent loss of control after take-off. Contributing to the accident was the pilot's failure to perform a hover check after lift-off, which would have alerted him to the pedal control anomaly at an altitude that could have allowed him to safely land the helicopter. Contributing to the severity of the injuries was the helicopter's fuel system, which was not crash resistant and facilitated a fuel-fed post-crash fire. What We Recommended ??To the Federal Aviation Administration: Require that existing Airbus Helicopters dual-hydraulic AS350-series helicopters be equipped with a visual and an aural alert for the loss of hydraulic boost to the pedal controls, which would result in increased pedal loads. To Airbus Helicopters: For newly manufactured dual-hydraulic AS350-series helicopters, assess and implement changes to the dual hydraulic system that would both ensure pedal control hydraulic assistance and mitigate the possibility of pilot error during any check of the hydraulic system. For existing dual-hydraulic AS350-series helicopters, assess and implement changes to the dual hydraulic system that would both ensure pedal control hydraulic assistance and mitigate the possibility of pilot error during any check of the hydraulic system.  South Sudan, Renk Airstrip: A Let L-410UVP-E8C Turbolet operated by the UN Upon landing at Renk Airport (HSRN), a UN LET L-410UVP-E8C Turbolet veered off the runway and got stuck in the mud. There were no personal injuries.  Democratic Republic of the Congo, Lubumbashi International Airport: An Ethiopian Airlines Boeing 787-9 Dreamliner, suffered a tail strike during an attempted landing at Lubumbashi Airport, D.R. Congo. The first approach to runway 07 was aborted at 12:54 UTC. The aircraft circled and landed on the second attempt at 13:10 UTC. It is unclear if the tail strike occurred during the first or second attempted landing. The aircraft was ferried unpressurised to Addis Ababa one day after the incident. Brazil, Comodoro, Mato Grosso: A Cessna 210 Centurion II crashed on landing in Comodoro, Mato Grosso. The police were called and found 510 kg of cocaine in two vehicles hidden in the bush. Two people were arrested. The pilot fled.  UK, Jackrells Farm Airfield, near Southwater, Horsham, West Sussex: Jodel DR.1050-M1 Sicile Record with two occupants clipped some trees and crashed while on approach to Jackrells Farm Airfield, near Southwater, Horsham, West Sussex. Both occupants were injured and taken to hospital and the aircraft was damaged beyond repair. Romania, Popoveni, Dolj County: A ICA Brasov IS-28B2 glider crashed in the garden of a house in Popoveni, Dolj County. The 17-year-old pilot, performing her first solo flight, was taken to hospital and the glider received substantial damage.   9 OCTOBER 1900 French aeronaut Count Henri de La Vaulx sets a world record for non-stop long-distance balloon flight. He flies for over 35 hours after taking off from Paris, France.  In 1898, he co-founded the Aero Club of France with Ernest Archdeacon, Léon Serpollet, Henri de la Valette, Jules Verne, Honorine de Viane Morel Verne, André Michelin, Albert de Dion, Alberto Santos-Dumont, and Henry Deutsch de la Meurthe. On Oct 9, 1900 he and a companion set a distance record in a balloon traveling 1200 miles from Vincennes to Korostishev near Kiev (then in Russia) in 35,75 hours. Also in 1900 he received the Grand Medal of the Aero Club of France for exceptional contributions to the progress of aviation. In 1905 he co-founded and became a director of the Fédération Aéronautique Internationale (FAI) The FAI now awards the De la Vaulx Medal, named for him. He visited the United States several times for ballooning ventures and the New York Times described him as one of the "most successful and daring balloonists in the world." He died when a scheduled flight between Montreal, Canada and Newark, NJ that he was on collided with power lines on approach to Newark on April 18, 1930, and was buried in the Rozoy-Bellevalle cemetery.  Beech 18 and DC3 to SAAF Museum AFB Swartkops Airshow 2015 Google Banner Ad  |
                             |
 |
 |

Copyright © Pilot's Post PTY Ltd
The information, views and opinions by the authors contributing to Pilot's Post are not necessarily those of the editor or other writers at Pilot's Post.